1. In computer
networking, cloud computing is computing that
involves a large number of computers connected through a communication network such
as the Internet,
similar toutility
computing. In
science, cloud computing is a synonym for distributed computing over
a network, and means the ability to run a program or application on many
connected computers at the same time. In
common usage, the term "the cloud" is essentially a metaphor for the
Internet. Marketers have further popularized
the phrase "in the cloud" to refer to software, platforms and
infrastructure that are sold "as a service", i.e. remotely through the Internet.
Typically, the seller has actual energy-consuming servers which host products
and services from a remote location, so end-users don't have to; they can
simply log on to the network without installing anything. The major models of
cloud computing service are known as software as a service, platform as a service, and infrastructure as a
service. These cloud services
may be offered in a public, private or hybrid network. Google, Amazon, IBM, Oracle Cloud, Rackspace, Salesforce, Zoho and Microsoft Azure are some well-known cloud vendors. Network-based
services, which appear to be provided by real server hardware and are in fact
served up by virtual hardware simulated by software running on one or more real
machines, are often called cloud computing. Such virtual servers do not
physically exist and can therefore be moved around and scaled up or down on the
fly without affecting the end user, somewhat like a cloud becoming larger or
smaller without being a physical object.
2. From the above explanation of cloud computing , there
are many benefits that we can take from cloud computing , namely
:\ Scalability , with cloud computing we can increase our storage capacity
without having to purchase additional equipment , such as hard drives , etc. .
We simply add the capacity provided by the cloud computing service providers .
-
Accessibility , we can access data
whenever and wherever we are , as long as we are connected to the Internet ,
making it easier for us to access the data when important .
-
Security , we can be assured ydata its
security by cloud computing service providers , so for IT based company , the
data can be stored securely in the cloud computing provider . It also reduces
the cost required to secure corporate data .
-
Creator , the user can do / develop their
creations or projects without having to submit their projects directly to the
company , but the user can send it through the cloud computing service
providers .
-
Anxiety , when a natural disaster strikes
our proprietary data stored safely in the cloud even though we damaged hard
drive or gadget
3. Here is how the data storage and
replication of data on the use of cloud computing technology . With Cloud
Computing is no longer a local computer should run the heavy computational work
required to run the application , no need to install a software package for
every computer , we only perform the installation of the operating system on
application . Computer networks that make up the cloud ( Internet )
handles them instead . This server will be running all applications ranging
from e - mail , word processing , to complex data analysis programs . When
users access the cloud ( internet ) for a popular website , many things can
happen . Users of Internet Protocol ( IP ) for example can be used to determine
where the user is located ( geolocation ) . Domain Name System ( DNS ) services
can then redirect the user to a server cluster that is close to the users so
that the site can be accessed quickly and in their local language . The user is
not logged into the server , but they login to their services using a session
id or cookie that has been obtained is stored in their browser . What users see
in the browser usually comes from a web server . Webservers run the software
and interface presents the user with the means used to collect orders or
instructions from the user ( click , type, upload , etc. ) These commands are
then interpreted by webservers or processed by the application server .
Information is then stored in or retrieved from a database server or file
server and the user is then presented with a page that has been updated . The
data is synchronized across multiple servers around the world for global access
quickly and also to prevent loss of data . Web
service has provided a general mechanism for the delivery of services , it
makes the service-oriented
architecture ( SOA ) is ideal to be applied . The goal of SOA is to address the
requirements of loosely coupled , standards-based , and protocol - independent
distributed computing . In SOA , software resources are packaged as a "
service , " a well-defined , self-contained modules that provide standard
business functionality and context of other services . Maturity web service has
enabled the creation of robust services that can be accessed on demand , in a
uniform way .
4. Cloud computing exhibits the following key
characteristics:
·
Agility improves with users' ability to re-provision
technological infrastructure resources.
·
Application programming
interface (API) accessibility to software
that enables machines to interact with cloud software in the same way that a
traditional user interface (e.g., a computer desktop) facilitates interaction
between humans and computers. Cloud computing systems typically use
Representational State Transfer (REST)-based
APIs.
·
Cost: cloud providers claim that computing costs reduce. A
public-cloud delivery model converts capital expenditure to operational expenditure. This
purportedly lowersbarriers to entry, as
infrastructure is typically provided by a third party and does not need to be
purchased for one-time or infrequent intensive computing tasks. Pricing on a
utility computing basis is fine-grained, with usage-based options and fewer IT skills
are required for implementation (in-house). The e-FISCAL project's
state-of-the-art repository contains
several articles looking into cost aspects in more detail, most of them
concluding that costs savings depend on the type of activities supported and
the type of infrastructure available in-house.
·
Device and location independence enable users to access systems using a web
browser regardless of their location or what device they use (e.g., PC, mobile
phone). As infrastructure is off-site (typically provided by a third-party) and
accessed via the Internet, users can connect from anywhere.
·
Virtualization technology allows sharing of servers and storage
devices and increased utilization. Applications can be easily migrated from one
physical server to another.
·
Multitenancy enables
sharing of resources and costs across a large pool of users thus allowing for:
·
centralization of infrastructure in locations with lower costs
(such as real estate, electricity, etc.)
·
peak-load
capacity increases (users need not engineer
for highest possible load-levels)
·
utilisation
and efficiency improvements for systems that are
often only 10–20% utilised.
·
Scalability
and elasticity via dynamic ("on-demand") provisioning of resources on a fine-grained, self-service
basis in near real-time(Note,
the VM startup time varies by VM type, location, os and cloud providers),
without users having to engineer for peak loads.
·
Performance is monitored, and consistent and loosely coupled
architectures are constructed using web services as the system interface.
·
Security can
improve due to centralization of data, increased security-focused resources,
etc., but concerns can persist about loss of control over certain sensitive
data, and the lack of security for stored kernels. Security is often as good as
or better than other traditional systems, in part because providers are able to
devote resources to solving security issues that many customers cannot afford
to tackle. However, the complexity of security is greatly increased when
data is distributed over a wider area or over a greater number of devices, as
well as in multi-tenant systems shared by unrelated users. In addition, user
access to security audit logs may be
difficult or impossible. Private cloud installations are in part motivated by
users' desire to retain control over the infrastructure and avoid losing
control of information security.
·
Maintenance of cloud computing applications is easier,
because they do not need to be installed on each user's computer and can be
accessed from different places.
5. Security in cloud computing
After exposure to the concept ,
technical , and architectural services builders in cloud computing , the next
concern is in terms of network security information. Cloud Computing is one of
the new technology remains to be seen what level of network security
information. Based on the model of services in cloud computing can be seen ,
whether the information network security loopholes are in the service model of
Software as a Service , and Platform as a Service , or , and nor does the
Infrastructure as a Service .
Furthermore, the security of cloud
computing can also be seen from its location on the protocols that govern data
communication in the network . Protocol which is used as a reference in this
paper is TCP / IP ( Transmission Control Protocol / Internet Protocol ) .
There are many security issues
surrounding cloud computing . With the technology that allows consumers to be
able to access cloud services through a web browser or web services , there are
three examples of security issues , namely : XML Signature Element Wrapping ,
Browser Security , Cloud Malware Injection Attack and Flooding Attacks.
From a research document issued by the
Cloud Security Alliance 's titled Top Threats to Cloud Computing , the two
security threats in cloud computing ie loss or data leakage and hijacking the
account or service . Two of these threats is crucial because it affects the
reputation , trust partners , employees , and customers also affecting business
. Piracy accounts can also be bad if Attackers accessing a very important part
of the cloud computing services , facilitate Attackers then to do things that
can affect aspects of confidentiality, integrity , and availability of servicing
existing service . To avoid the above types of security threats , identity
management and access control are the main requirements for SaaS Cloud
computing Company .
Identity Management in the cloud
computing are also associated with the focus of discussion in this paper , the
security of the cloud computing service model of Software as a Service it .
With a detailed explanation of the components before forming a SaaS Cloud
Computing is using Service Oriented Architecture ( SOA ) with Web Services
standards ( XML language ) .
Identity management and access control in cloud
computing Service Oriented Architecture
As defined earlier , the SOA has
features that make loosely-coupled SOA is very open to security risks that can
occur . Therefore, SOA must meet several key requirements to meet data security
standards , among other things: service discovery , service authentication ,
user authentication , access control , confidentiality, integrity ,
availability , and privacy ( 17 ) . To ensure security in SOA development
environment , which creates a community of open standards to build a web
services security standard for Web services , which is known implementations of
web services is the most widely used SOA . At the same time the identity
management and access control in cloud computing has also arranged with the
standard .
As shown in the image above , for
controlling access rights has been the adoption by the Security assertion
markup language ( SAML ) and the eXtensible Access Control Markup Language (
XACML ) , meaning that when a user requests a service , the user must follow
the security policies related to access control established .
SAML and Single Sign On
SAML is an XML standard for exchanging
authentication and authorization of data between security domains. SAML
features platform independent , and is mainly applied to the Single Sign -On (
SSO ) . Single Sign-On is one of the methods used in data security aspects of
authentication and authorization on the application or cloud service .
Technology Single - sign-on ( SSO ) is a technology that allows users to easily
access network resources in a network using only one user account only. This
technology is in high demand , especially in very large networks and
heterogeneous ( in current operating systems and applications used by computers
is derived from many vendors , and users are asked to fill in the information
itself into each of the different platforms to be accessed by users ) . By
using SSO , a user just simply attempt to authenticate only once to obtain
permits access to all the services contained within the network .
SaaS Cloud Computing Security with Single Sign On in a
layer Internet Protocol
TCP / IP
From the description of the overall architecture of
SaaS Cloud Computing can be mapped position SaaS Cloud Computing Security with
Single Sign On in layer Internet protocol TCP / IP , so it is more clear
understanding of network security information as part of a network of
information science itself. Mapping architecture can be seen in the image
below:
6. Cloud Computing is the result of evolution and
adoption of existing technologies and paradigms. The goal of cloud computing is
to allow users to take benefit from all of these technologies, without the need
for deep knowledge about or expertise with each one of them. The cloud aims to
cut costs, and help the users focus on their core business instead of being
impeded by IT obstacles.
The main enabling technology for cloud computing
is virtualization.
Virtualization generalizes the physical infrastructure, which is the most rigid
component, and makes it available as a soft component that is easy to use and
manage. By doing so, virtualization provides the agility required to speed up
IT operations, and reduces cost by increasing infrastructure utilization. On the other hand, autonomic computing automates
the process through which the user can provision resources on-demand. By minimizing user involvement, automation speeds
up the process and reduces the possibility of human errors.
Users face difficult business problems every day.
Cloud computing adopts concepts from Service-oriented
Architecture (SOA) that can help the user break these problems
intoservices that
can be integrated to provide a solution. Cloud computing provides all of its
resources as services, and makes use of the well-established standards and best
practices gained in the domain of SOA to allow global and easy access to cloud
services in a standardized way.
Cloud computing also leverages concepts from utility
computing in order to provide metrics for the
services used. Such metrics are at the core of the public cloud pay-per-use
models. In addition, measured services are an essential part of the feedback
loop in autonomic computing, allowing services to scale on-demand and to
perform automatic failure recovery.
Cloud computing is a kind of grid computing; it has evolved by addressing the QoS (quality
of service) and reliability problems.
Cloud computing provides the tools and technologies to build data/compute
intensive parallel applications with much more affordable prices compared to
traditional parallel computing techniques.[35]
Cloud computing shares characteristics
with:
·
Grid computing — "A form of
distributed and parallel computing, whereby a 'super and virtual computer' is
composed of a cluster of
networked, loosely coupled computers
acting in concert to perform very large tasks."
·
Utility computing — The "packaging
of computing resources,
such as computation and storage, as a metered service similar to a traditional
public utility, such as electricity."[38][39]
·
Peer-to-peer — A distributed architecture without the
need for central coordination. Participants are both suppliers and consumers of
resources (in contrast to the traditional client–server model).
·
Cloud gaming — Also known as on-demand gaming, is a way
of delivering games to computers. Gaming data is stored in the provider's
server, so that gaming is independent of client computers used to play the
game. One such current example, would be a service by OnLive which
allows users a certain space to save game data, and load games within the
OnLive server.
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cloud_computing
http://id.wikipedia.org/wiki/Komputasi_awan
http://royanafwani.wordpress.com/2011/12/22/keamanan-pada-cloud-computing/
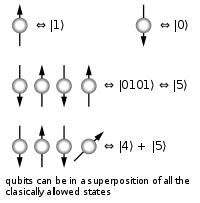
 different three-bit strings 000, 001, 010, 011, 100, 101, 110, 111. If it is a deterministic computer, then it is in exactly one of these states with probability 1. However, if it is a
different three-bit strings 000, 001, 010, 011, 100, 101, 110, 111. If it is a deterministic computer, then it is in exactly one of these states with probability 1. However, if it is a 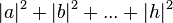 , that must equal 1. These square magnitudes represent the probability amplitudes of given states. However, because a complex number encodes not just a magnitude but also a direction in the
, that must equal 1. These square magnitudes represent the probability amplitudes of given states. However, because a complex number encodes not just a magnitude but also a direction in the  , the probability of measuring 001 =
, the probability of measuring 001 =  , etc..). Thus, measuring a quantum state described by complex coefficients (a,b,...,h) gives the classical probability distribution
, etc..). Thus, measuring a quantum state described by complex coefficients (a,b,...,h) gives the classical probability distribution  and we say that the quantum state "collapses" to a classical state as a result of making the measurement.
and we say that the quantum state "collapses" to a classical state as a result of making the measurement.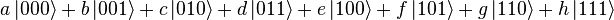

 and
and 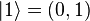 .
. and
and  .
.